Explore the Daily Current Affairs 30 September 2025, relevant for UPSC exam. Download quick REVISION NOTES.
South-South and Triangular Cooperation (SSTC)
South‑South Cooperation: South‑South Cooperation refers to collaboration among countries of the Global South, mainly developing or emerging economies, in political, economic, social, cultural, environmental, or technical domains.
What is Triangular Cooperation (TrC)?
Triangular Cooperation involves a partnership among three actors:
- Two or more developing countries (South-South partners)
- One developed country or multilateral organization (as a facilitator or supporter)
What is SSTC (South-South and Triangular Cooperation)?
SSTC combines South-South Cooperation (SSC) and Triangular Cooperation (TrC). It means, Developing countries lead the projects and a third partner (like the UN, Japan, or the EU) provides financial resources, technical expertise, or capacity-building support.
| Example of SSTC |
|---|
| Project: Improving Rice Farming in Africa India – shares rice farming techniques. African countries – like Senegal implement the methods. Japan – (through JICA) funds the training and equipment. This is SSTC: India (South) + Africa (South) + Japan (Third Partner). |
India’s Leadership in SSTC:
India is a leading example of how SSTC can work in practice.
India’s Key Contributions:
- Promotes Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam (“The world is one family”).
- Hosted Voice of the Global South Summits.
- Advocated for African Union membership in the G20.
- Runs the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program, building capacity in over 160 countries.
- Created the India-UN Development Partnership Fund.
- Promoted tech like Aadhaar, UPI, and digital governance globally.
- Supports plurilateral cooperation platforms (e.g. BIMSTEC, IBSA).
Mains practice question:
Q1. “South-South and Triangular Cooperation (SSTC) is more than a diplomatic phrase; it is a practical tool for achieving sustainable development and global equity.” Discuss
Generation Gap
Key Highlights of article:
- 10% of Indians are currently above 60 years of age, projected to rise to 20% by 2050.
- Loneliness is a shared concern: ~69% of youth and 68% of elders cite it as a major issue.
3. Digital divide is a major factor worsening the disconnect among elderly and youth. Elders want to learn technology but lack supportive environments. Youth wrongly assume disinterest or incompetence for elderly.
4. Family-centric living is still valued, but significant portion of youth (30%) are open to care homes (for elderly), compared to only 19% of elders.

Source: The Hindu newspaper (Page no. 7)
Feminisation of Agriculture
Article highlights the role of women in Indian agriculture and the challenges they face.
Key Issues:
- Feminisation of Agriculture:
- Women now constitute over 42% of the agricultural workforce.
- Unpaid female labour increased drastically – now 1 in 3 working women is unpaid.
- Despite high participation, economic returns are low, showing systemic inequity.

2. Structural Inequities:
- Land ownership: Women own only 13-14% of land.
- Wage gap: Women earn 20-30% less than men for similar work.
- Limited access to credit, schemes, and decision-making power.

Way forward:
- Recognition & Ownership: Formal recognition of women as farmers with land rights is fundamental to improving their economic status.
- Skill & Capacity Building: Training in digital literacy, business skills, and value-addition processes can empower women to transition from unpaid laborers to entrepreneurs.
- Leveraging Trade: Support mechanisms (credit, training, market access) embedded within trade agreements could boost women-led agri-businesses.
- Technology Inclusion: Expanding affordable, multilingual, voice-enabled digital tools tailored for women could bridge access gaps effectively.
- Collaborative Ecosystem: Government, NGOs, private sector, and farmer groups need to collaborate to scale up successful models.
Success Stories & Best Practices:
- Odisha’s Swayam Sampurna FPOs
- Jhalawari Mahila Kisan Producer Company, Rajasthan
- Digital Sakhi Program (L&T Finance)
- Tea sector reforms in Assam

Source: The Hindu newspaper (Page no. 8)
Mental Health Scenario in India
WHO Data Insights
- WHO estimates that the burden of mental health problems in India is 2443 disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) per 10000 population;
- the age-adjusted suicide rate per 100000 population is 21.1.
- The economic loss due to mental health conditions, between 2012-2030, is estimated at USD 1.03 trillion.
Prevalence:
- The National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) 2015-16 by NIMHANS found that 10.6% of adults in India suffer from mental disorders.
- The lifetime prevalence of mental disorders in India is 13.7%.
- National studies reveal that 15% of India’s adult population experiences mental health issues requiring intervention.
- Urban areas have a higher prevalence (13.5%) compared to rural (6.9%).
Treatment Gap
- 70% to 92% of people with mental disorders do not receive proper treatment due to lack of awareness, stigma, and shortage of professionals.
- According to the Indian Journal of Psychiatry India has 0.75 psychiatrists per 100,000 people, whereas WHO recommends at least 3 per 100,000.
Economic Survey 2024-25 recommendations:
- Enhance Mental Health Education in Schools: Early intervention strategies to address anxiety, stress, and behavioural issues in students.
- Improve Workplace Mental Health Policies: Address job stress, long working hours, and burnout.
- Expand Digital Mental Health Services: Strengthen Tele MANAS and integrate AI-based mental health solutions.

Mains practice Question:
Q2. Despite progressive legislation and digital initiatives, India continues to face a massive mental health treatment gap. Discuss the challenges in delivering mental healthcare in India and suggest a multipronged approach to bridge these gaps.

Source: The Hindu newspaper (Page no. 12)
India-Bhutan railway link
Railway projects has been announced to link:
- Kokrajhar (Assam) – Gelephu (Bhutan)
- Banarhat (West Bengal) – Samtse (Bhutan)
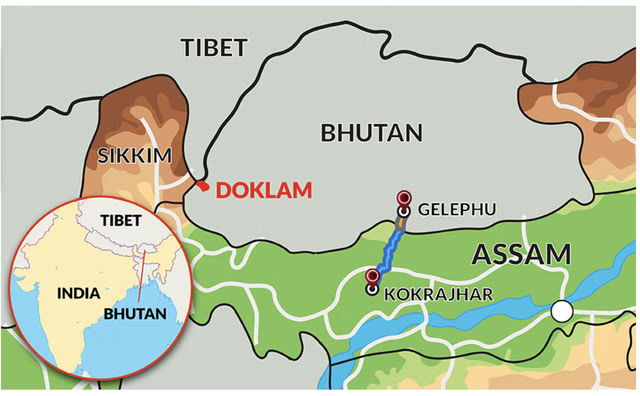
Total length: 89 km
Total cost: ₹4,033 crore
These are the first railway lines between India and Bhutan, marking a new phase in bilateral ties.
Neighbourhood First Policy in action:
- Strengthens India’s traditional and trusted relationship with Bhutan.
- Reinforces India’s position as a preferred development partner.

Geopolitical implications:
- Counters China’s growing influence in Bhutan (especially near the Doklam Plateau).
- Establishes India’s role as Bhutan’s gateway to the world, ensuring Bhutan’s dependence on India for trade and transit.
- India has pledged support of ₹10,000 crore for Bhutan’s 13th Five Year Plan (2024–2029), covering Project Tied Assistance (PTA), High Impact Community Development Projects (HICDP), the Economic Stimulus Programme (ESP), and budgetary support through Programme Grants.


